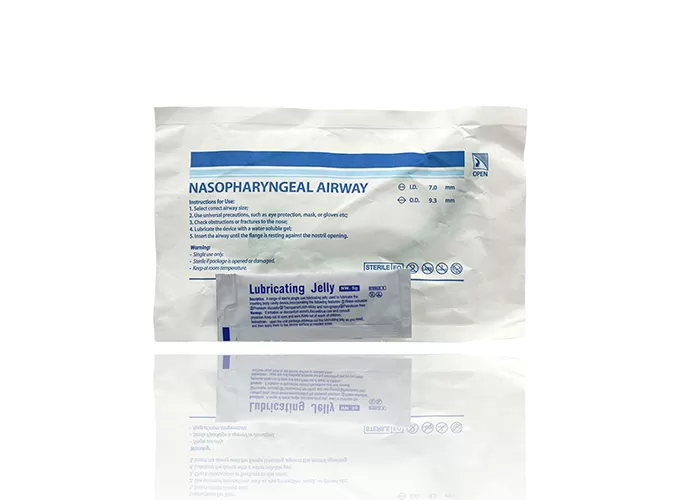
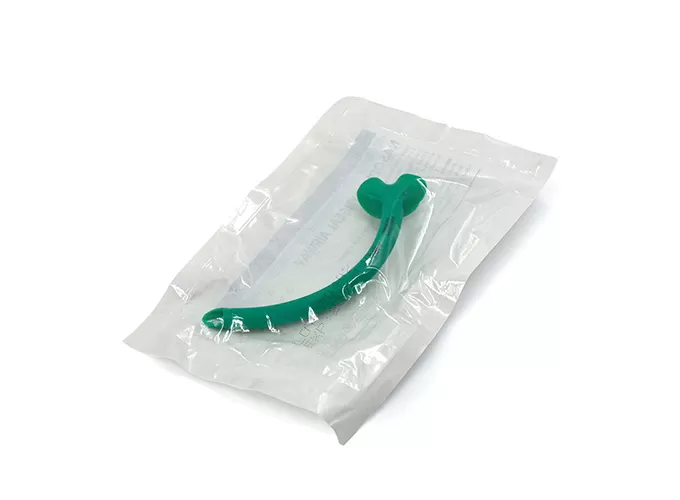
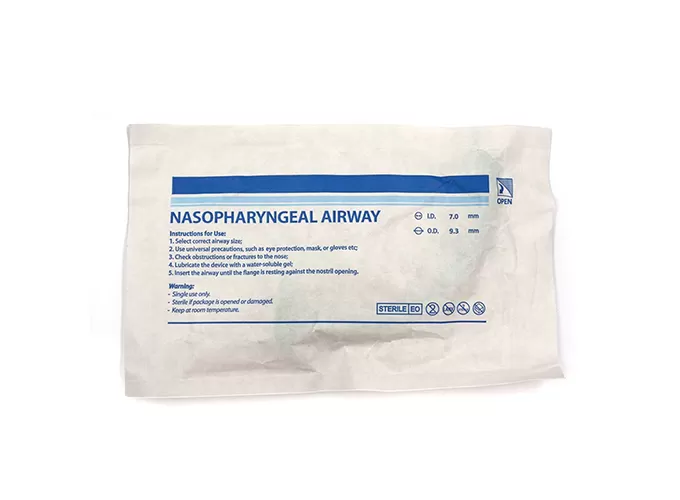
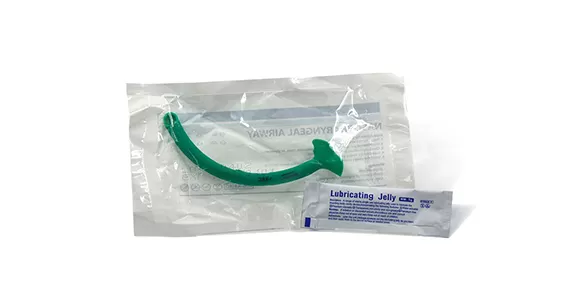
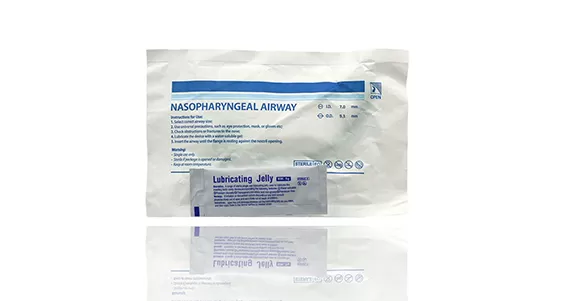
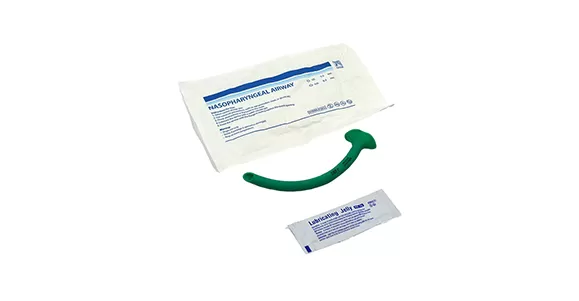
Products
- Medical Dressings and Bandaging Products
- Medical Waste Disposal Products
- In Vitro Diagnostic Reagents
- Respiratory Products
- Urology Products
- Infusion Products
- Operating Room Infection Control Products
- Commercial Medical Consumables
- Anesthesia Products
- First Aid Products
- Personal Care Products
- Rehabilitation Products
- Home Medical Equipment
- Animal Test Kits
- Animal Infusion Products
- Animal Diagnostic Equipment
- Animal Medical Consumables
What are you looking for?