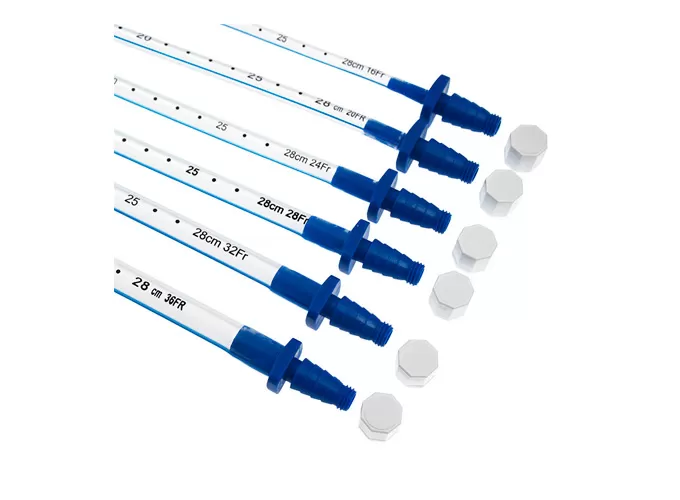
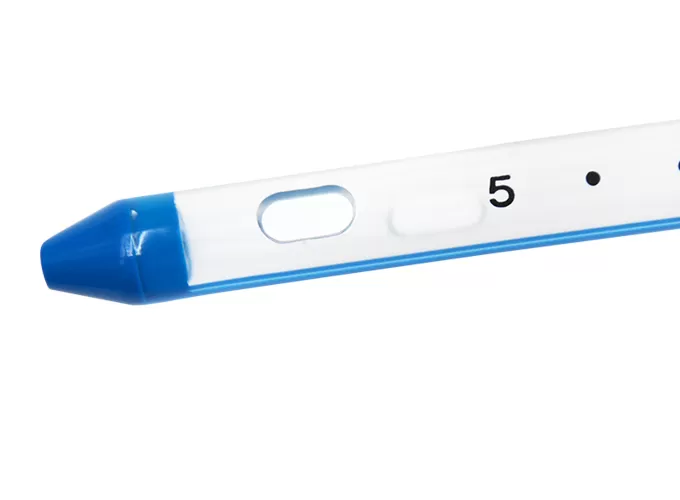
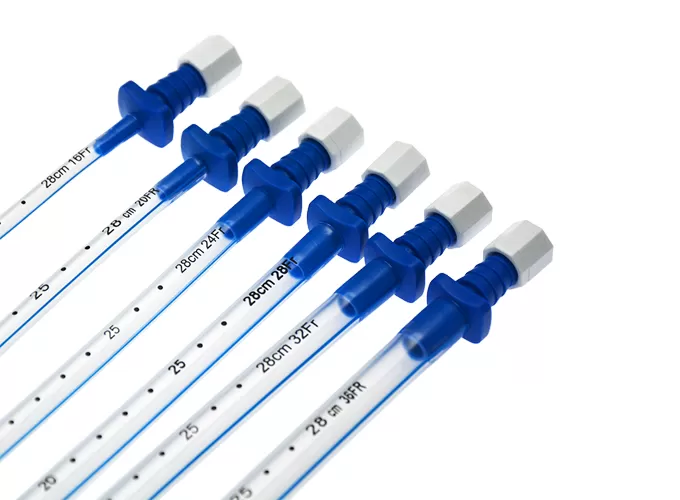
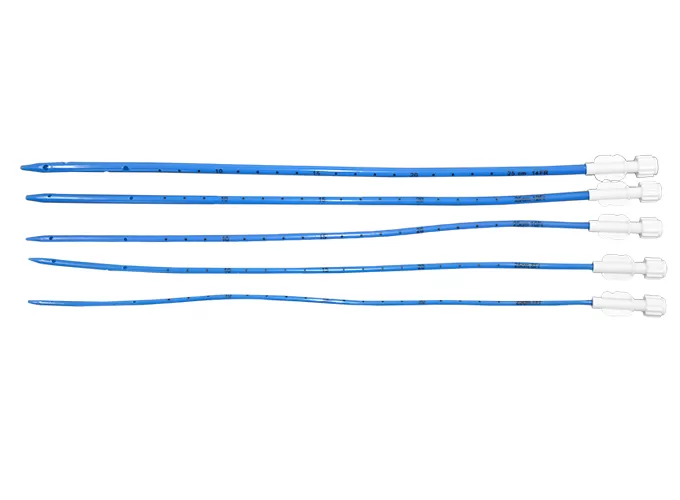
Steps for Using a Chest Drainage Catheter
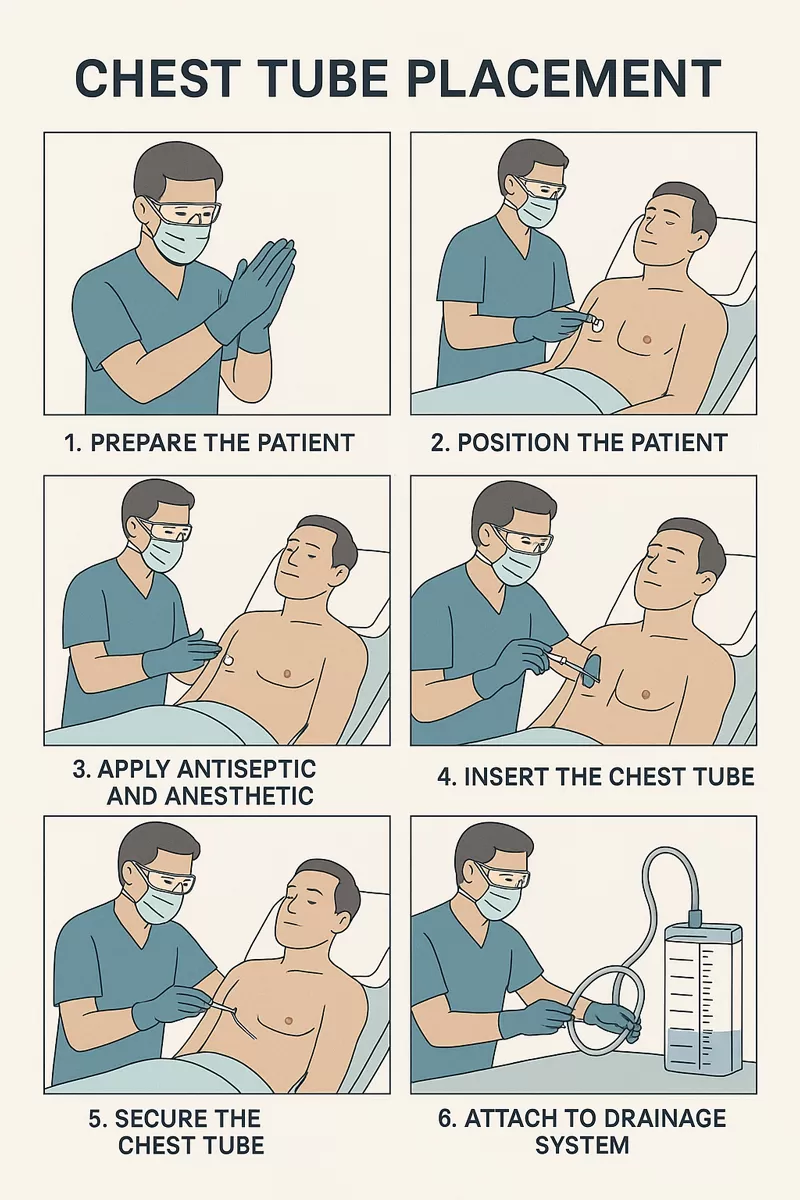
1. Preparation and Equipment Check
Ensure all necessary equipment is available and functional: sterile chest tube set, drainage system, local anesthetic, scalpel, forceps, suture, and dressing.
Explain the procedure to the patient and obtain informed consent.
Position the patient in a semi-recumbent or supine position with the arm raised above the head to expose the insertion site.
Perform hand hygiene and don sterile gloves, gown, and mask.
2. Site Identification and Aseptic Preparation
Identify the appropriate intercostal space, usually the 4th or 5th intercostal space, mid-axillary line.
Disinfect the skin thoroughly and drape the site in a sterile fashion.
3. Local Anesthesia and Incision
Infiltrate local anesthetic down to the pleura at the chosen insertion site.
Make a 2–3 cm horizontal incision above the rib margin to avoid the neurovascular bundle.
4. Insertion of the Chest Tube
Bluntly dissect through the subcutaneous tissue and intercostal muscles with a curved clamp until the pleural space is entered.
Insert a finger to confirm pleural entry and check for adhesions.
Insert the chest tube into the pleural space, directing it posteriorly and superiorly for pneumothorax, or inferiorly for effusion/hemothorax.
5. Securing and Connecting the System
Secure the tube to the skin with sutures and apply a sterile dressing.
Connect the tube to a water-seal or suction drainage system as indicated.
Ensure the drainage system is below chest level and functioning properly.
6. Post-Insertion Care and Monitoring
Confirm tube position and lung re-expansion via chest X-ray.
Monitor for complications such as air leaks, infection, or tube blockage.
Record drainage amount and characteristics regularly.
Applications of Chest Drainage Catheter
1. Hospitals and Clinics
Used in emergency rooms, respiratory departments, pediatric units, and outpatient clinics for the treatment of asthma, COPD, bronchitis, and other respiratory conditions.
2. Home Healthcare Settings
Ideal for patients undergoing long-term respiratory therapy at home. The mask offers a convenient, user-friendly solution for self-administered nebulization under medical supervision.
3. Pediatric and Geriatric Care
Special sizes are available for infants, children, and elderly patients, ensuring safe and effective medication delivery across different age groups.
4. Emergency and Pre-Hospital Care
An essential part of respiratory kits in ambulances and mobile medical units. Provides rapid aerosolized medication delivery in acute respiratory distress cases.
5. Postoperative and Recovery Rooms
Supports patients with breathing difficulties during recovery after surgery or anesthesia, especially when aerosolized bronchodilators or steroids are required.
6. Nursing Homes and Rehabilitation Centers
Widely used for elderly patients with chronic respiratory diseases, helping manage symptoms and improve quality of life.
7. Temporary Medical Facilities and Field Hospitals
Applicable in disaster response scenarios, quarantine zones, or remote medical stations where portable and reliable respiratory equipment is needed.
8. High-Risk Infection Control Zones
Can be used in isolation rooms or COVID-related wards to administer medication while minimizing contact and cross-contamination risks.